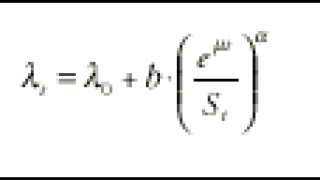Learning Curve
-
In this Learning Curve we describe the latest developments in credit derivative-based synthetic funding structures, which are now being used for liquidity and balance sheet asset-liability management by banks and other financial institutions.
-
A range structure accrues value when a reference index fixes inside a specific range during a pre-defined period.
-
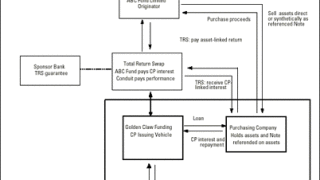
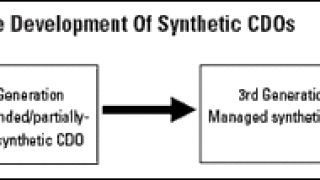
The synthetic collateralized debt obligation is well-established as a vehicle used to facilitate balance sheet capital management, credit risk transfer and credit trading.
-
This week's Learning Curve focuses on non-deliverable options and the potential of the Chinese derivatives market.
-
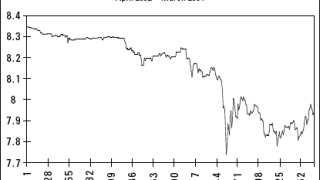
Few issues have attracted as much attention worldwide as the Chinese yuan (CNY) or renminbi (RMB) has done in the past two years.
-
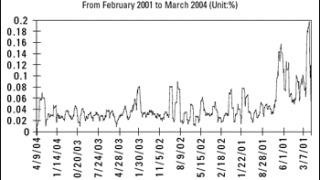
The Japanese credit-default swap market, as with many credit markets, has grown rapidly over the past five years.
-
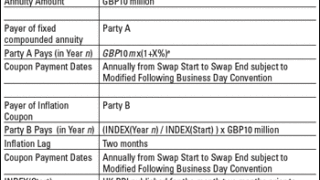
Project finance or long-term rental agreements often involve fees that are fixed at a certain real level over the life of the trade: the annual payment is a fixed amount adjusted by the cumulative inflation since trade inception.
-
This week's Learning Curve deals with the types of market participant, geographic variations and two of the most popular instruments: zero-coupon swaps and year-on-year swaps.
-
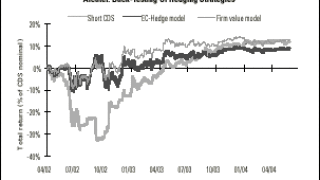
An attractive feature of the EC-Hedge (equity-credit hedge) model is its ability to use equity implied volatility as an input data.
-
Strategies involving both equity and credit products have become increasingly popular, under the pressure of both an overall decrease in market volatility and structural changes among alternative investment strategies.
-
Last week's article gave a general introduction into Regulation SHO and looked at a pilot program suspending a price test for specified securities and the uniform locate requirement.
-
The Securities and Exchange Commission published Regulation SHO on July 28.